크게 보려면 그림을 클릭하세요.
| 슬라이드 1 | ||
| 슬라이드 2 | ||
| 슬라이드 3 | ||
| 슬라이드 4 | ||
| 슬라이드 5 | ||
| 슬라이드 6 | ||
| 슬라이드 7 | ||
| 슬라이드 8 | ||
| 슬라이드 9 | ||
| 슬라이드 10 | ||
| 슬라이드 11 | ||
| 슬라이드 12 | ||
| 슬라이드 13 | ||
| 슬라이드 14 | ||
| 슬라이드 15 | ||
| 슬라이드 16 | ||
| 슬라이드 17 | ||
| 슬라이드 18 | ||
| 슬라이드 19 | ||
| 슬라이드 20 | ||
| 슬라이드 21 | ||
| 슬라이드 22 | ||
| 슬라이드 23 | ||
| 슬라이드 24 | ||
| 슬라이드 25 | ||
| 슬라이드 26 | ||
| 슬라이드 27 | ||
| 슬라이드 28 | ||
| 슬라이드 29 | ||
| 슬라이드 30 |
Neurogenic bladder
Injury at the S2-S4 level can result in impairment of detrusor contractility and malfunction of pudendal nerves, which innervate the distal sphincter.
Involuntary detrusor contraction (IDC) after an injury at the C2-S1 region and open fixed tone of the distal sphincter by denervation after S2-S4 injury can induce storage failure.
In addition, detrusor-sphincter dyssynergia (DSD) after C2-S1 injury and detrusor underactivity (DU)/detrusor acontractility (DA) or nonrelaxing urethral sphincter obstruction after S2-S4 injury can result in failure to empty.
Because the nuclei of the pelvic nerves involved in contraction of the detrusor muscle and the pudendal nerves responsible for contraction of the striated sphincter are located in different portions of the sacral cord (intermediolateral cell column vs ventral gray matter), sacral SCI can induce DA, leaving striated sphincter function intact.
Normal study. FD = First Desire to Void, ND = Normal desire to void, SD = Strong desire to void, U = Urgency, CC = Cystometric Capacity (permission to void given).
52 year old female with urgency and frequency. Phasic detrusor activity during filling. Leakage is associated with urgency and detrusor contractions. FD = First Desire to Void, ND = Normal desire to void, SD = Strong desire to void, U = Urgency, L = leakage, MCC = Maximum Cystometric Capacity.
DH, DSD
Fig. 2. Reflexes of the neuropathically damaged bladder. A, aberrant pelvic and pudendal reflexes following spinal injury causing detrusor hyper-reflexia (DH) and detrusor sphincter dyssynergia (DSD). B, urodynamics showing high detrusor pressures, sphincter overactivity and incontinence associated with DH and DSD.
Figure 1 Detrusor overactivity, detrusor-sphincter dyssynergia and high voiding pressure in a child with occult spinal dysraphism.
'Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation > ASSOCIATED TOPICS IN PHYSICAL MEDICINE AND REHABILITATION' 카테고리의 다른 글
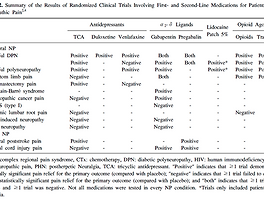
| 신경병증성 통증의 치료 (0) | 2014.11.03 |
|---|---|
| FIM instrument (0) | 2014.01.24 |
| Wheelchair 휠체어 (0) | 2010.03.30 |
| 통증에 대한 정의 & 경피전기신경자극치료 (0) | 2010.02.01 |
| Pseudodementia (0) | 2010.01.28 |